Measurement process is one of the most important issues during wind turbine generator (WTG) and wind power plant (WPP) evaluation and requires careful approach. Accurate measurements of harmonic voltages and currents in offshore WPPs followed by proper data analysis are essential for harmonic emission evaluation. In harmonic measurements it is of great importance to specify appropriate measurement points and optimize data acquisition devices as well as sensors.
Measurement systems involving multiple devices often require accurate timing in order to secure event synchronization and correlation in long-term data acquisition. One of the ways to achieve this synchronization measurement units must synchronize their individual clocks in order share a common time base. In large offshore WPPs distributed clock synchronization becomes necessary. Distributed clock synchronization in WPPs requires devices synchronized to a GPS satellite because of significant distances between measurement units [1].
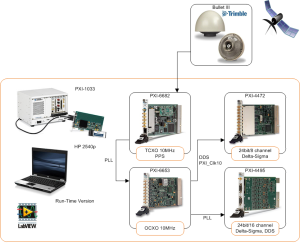
As presented in Figure 1 there are two synchronization possibilities: (1) with reference clock and (2) by means of phase-locked loop (PLL) synchronization.
(1) With the reference clock , the PXI 4472 device locks their frequency timebases – the inputs of their direct digital synthesis (DDS) chips, to the PXI_Clk10 (10 MHz) clock supplied by the PXI unit backplane. This is accomplished by using PLL. After a sync pulse is sent, which aligns the sample clock timebase on each device, the oversample clocks, and the analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). Finally, a shared start trigger is sent, which starts the acquisition and generation events on each device at the same instant.
(2) Another synchronization is just done by means of PLL which provides sufficient accuracy for harmonic measurements. Having an appropriate synchronization the GPS disciplined oscillator (GPSDO) is used to combine the good short term stability of the crystal oscillator with the excellent long term stability of the GPS signal. It assures that each acquired sample by all dispersed measurement unit will be synchronized together as presented in Figure 2.
In order to achieve that GPS synchronized triggering and GPS disciplined timebase were used. As an exemplary configuration PXI-6682, PXI-6653, PXI-4495 and PXI-4472 can be used in each of measurement locations in order to assure precise synchronization and high quality (i.e. aliasing free, high resolution equal to 24 bits, suitable sample rate equal to 44.1kS/s/ch) data acquisition [2].
[1] Ł. H. Kocewiak, I. Arana, J. Hjerrild, T. Sørensen, C. L. Bak, and J. Holbøll, "GPS Synchronization and EMC of Harmonic and Transient Measurement Equipment in Offshore Wind Farms," Energy Procedia, vol. 24, pp. 212-228, 2012.
[2] Ł. H. Kocewiak, A. Baloi, “Evaluation of Power Quality Monitoring Systems in Offshore Wind Farms,” in Proc. The 13th International Workshop on Large-Scale Integration of Wind Power into Power Systems as well as Transmission Networks for Offshore Wind Farms, Energynautics GmbH, 11-13 November 2014, Berlin, Germany.